Introduction
Location Map
Base Map
Database Schema
Conventions
GIS Analyses
Flowchart
GIS Concepts
Results
Conclusion
References
A GIS Application for Trail Suitability within
Bale Mountain National Park, Ethiopia
GIS Analysis
Trail suitablity was established by asigning arbitrary point values based on the pre-defined parameters for preferable trail locations. Raster dataset layers were overlaid on to one another to show areas exibiting positive point values indicating parameter suitablity. This in turn delineates spatial extent of desirable physical attributes of the landscape.
We added established areas and transportation routes in order to show the suitable trail areas so our map is descernable to a broader audience.
Below are the various tools used in ArcMap. See GIS Concepts for additional information and descriptions of each technique used to extract and process information. Always remember where you save and what you called your data layers.
Sort by Attribute
- In order to search for a particular attribute right click on the layer you wish to look.
- Then open Attribute Table/Options/Attribute table/Select which attributes you would like to look at and click apply.
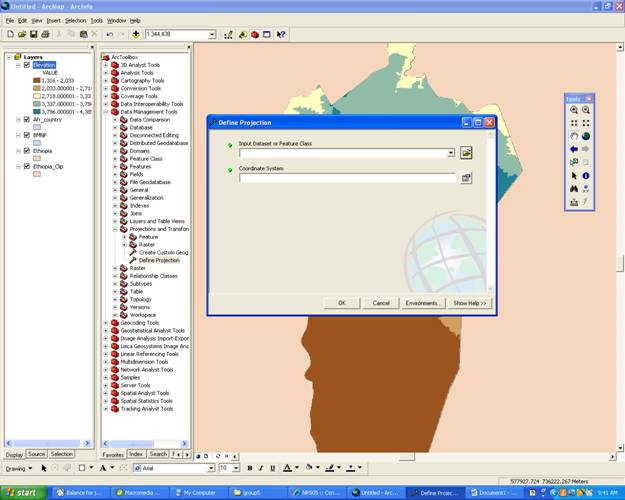
Define Projection
- Within ArcToolbox click Data Managment Tools/Pprojections and Transformations/Define Projection
- Then choose what feature class you would like to define and click ok
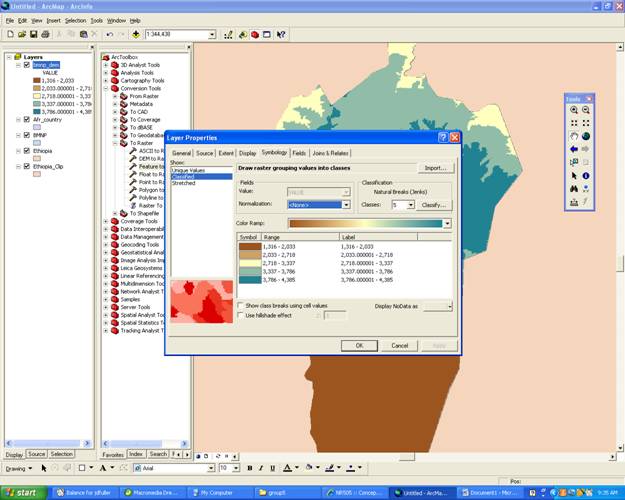
Re-Classify
- To re-classify your data layer right click on the desired layer and scrole down to properties
- Click on Symbology/Classify/Classes (change to desired numerical value) Click OK.
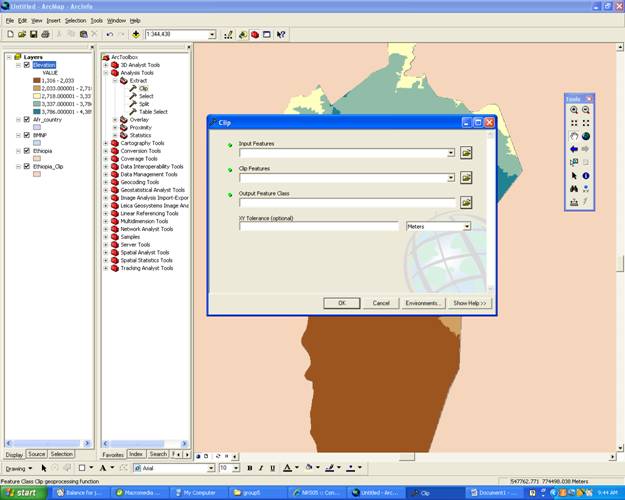
Clip
- To Clip an area to create a smaller Base map go into ArcToolbox under Analysis Tools/Extract/Clip
- Within the clip page choose the large file of the input feature and the clip feature is the smaller area you wish to focus on.
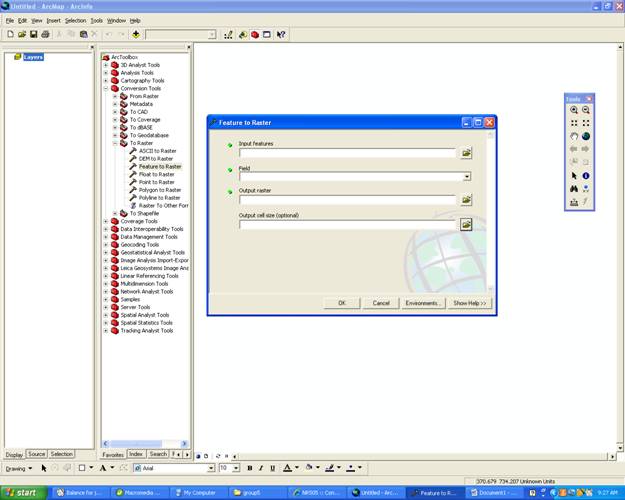
Vector To Raster
- Vector and Raster layers do not overlay on eachother accurately so they must be converted to a similar set. To convert vector to raster go into the ArcToolbox then Conversion Tools/To Raster/Feature to Raster.
- Fill in the feature you would like to convert. The field refers to what part of the feature you want to convert and output again is where to save the new data.
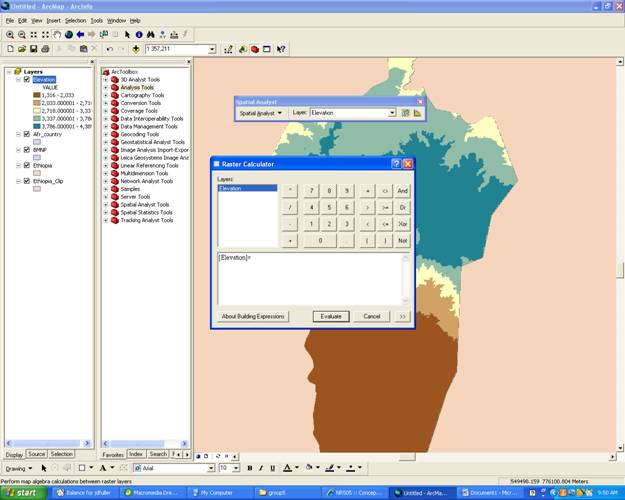
Raster Calculator
- The raster calculater can be used to overlay maps using binary values. Once your maps symbology is changed to 0, 1 (undesirable, desirable). Open the Spatial Analyst (View/tools/spatial analyst also go into Tools/Extentions/check Spatial Analyst)
- Under the Spatial Analyst Tool Bar Select Raster Calculator and create an equation of the two maps you would like to join which equals your new map. For example [Elevation]*[Slope]=[Hiking_areas]
- Evaluate.