
-
Laboratory Activities
- Modified Whittaker Plot
- Intensive Modified Whittaker Plot
- Nested Pixel Plot
- P-Plot
- C-Plot
- Beyond NAWMA Circle
Tips
GPS
Invasive Species Exercises: Beyond NAWMA Circle
This invasive species monitoring plot meets the North American Weed Management Association's (NAWMA) mapping standards and data requirements for efficient data comparability and sharing.
The Beyond NAWMA standards increase the value of invasive species data through sensitivity to change in pattern and species composition over time.
This circular plot allows for sampling at varying scales and resolutions, as well as at different angles within the circle, resulting in a diverse representation of data across spatial and temporal scales.
Setting up the Beyond NAWMA Circle
Equipment needed:
- 16 pin flags or stakes
- GPS unit to determine locations and azimuths
- Palm Pilot PDA with EcoNab
- DBH Tape for tree measurements
- 1-square meter quadrat frame (optional)
Setup:
- Before locating the plot, take each subplot/quadrat frame, and paint 10 cm sections, to calibrate the frame
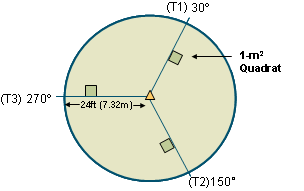
- Locate the predetermined plot and flag the center point
- Determine the 30, 150, and 270-degree azimuths from the center of the plot
- For each azimuth, create a transect 24 feet in length from the center point and flag the 24-foot mark to delineate the perimeter of the plot
- Along each transect, place 1-square-meter subplots between the 15 and 18.3-foot marks. Flag the four corners of each subplot, or place a frame for the subplots
- For each 1-square meter subplot, record species identification and dominant microhabitat codes and percent cover estimated to the nearest 1% for each plant species and microhabitat
- Identify each plant species present in the subplot, and then enter its corresponding Natural Resource Conservation Serivce (NRCS) PLANTS database code
- Then, estimate percent cover to the nearest percent for each species
- Estimate percent cover for each ground variable in the Microhabitat Variables Table below
Microhabitat Variables Code Dead wood, log, and slash Dung Fungus Lichen Litter / Duff; accumulation of organic matter over forest mineral soil Live root / bole; living roots at the base of trees or exposed at the surface of the forest floor or soil and cross-sectioned area of live tree boles at the ground line Mineral soil / sediment; physically weathered soil parent material that may or may not also be chemically and biologically altered Moss Road Rock; large rock or boulder, or accumulation of pebbles or cobbles Standing water / flooded; ponding or flowing water that is not contained within banks Stream; body of flowing water contained within banks Trash / junk
Estimating Cover:
- Only estimate percent cover for plants that are entirely located within the frame. If only part of a plant is inside the frame, estimate the cover of that portion of the plant in the frame, not the entire plant
- Get to know about how much 1%, 5%,and 10% cover look like, so that you can easily reference things like the size of your hand, etc. to estimate percent cover in the field
- NOTE: there will often be overlap in a subplot, so it is possible for your total percent cover estimate to exceed 100
- After estimating cover for each subplot, walk the rest of the plot, looking for any new species that were not present in the subplots. Add these new species to the species list for that sample
Data Collected:
- UTM location of the center stake in the plot
- Trees >10 cm in DBH at 2.3 m above the ground; record the DBH values of these trees by species (live and dead trees recorded separately)
- Tally trees <10 cm; record DBH values by species
- Total tree canopy cover (estimated to the nearest 5%)
- Topographic position (slope, aspect, elevation, etc)
- Distance to stream (or water), distance to road, and distance to crops if distances are <100 m
- Land use notes on disturbance, grazing intensity, small mammal mounds, etc. that make sense for data analysis of plots
Optional Add-ons:
- Collect soil samples after litter is removed
- four soil samples (one in the center of the plot, and one for each point where the transects intersect with the perimeter of the plot)
- Take samples with a 2.5-centimeter core to a depth of 15 centimeters
- Analyze samples for texture, total Nitrogen and total Calcium, and other appropriate nutrients
- Permanent Stake
- Install a copper top-engraved survey stake for long-term monitoring at the study site
- Permanent pins can be used at the four corners of each subplot along the transects as well
- Collect and store data with a Microsoft Access-compatible application or software program that can be loaded onto a handheld computer and interface with a GPS unit, to obtain efficient movement of data from the field to the lab for analysis.
-
Stohlgren T.J., Barnett D.T. & Crosier C.S. (2005) Beyond NAWMA - The North American Weed Management Association Mapping Standards. In Progress.
The National Institute of Invasive Species Science